Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, more famously known by its abbreviation – CPR, is recognized as a crucial life-saving skill that can greatly impact the victim’s survival in emergencies, such as out-of-hospital heart arrest. In fact, only 1 out of 10 people experiencing cardiac arrest out of hospital survive. However, the CPR technique can double and even triple the survival chance of the victim by performing CPR promptly as an emergency response in the first couple of minutes after a cardiac arrest.
There are a couple of variations to the CPR technique that can serve as an immediate response to cardiac arrest, ranging from the classic CPR emergency response with rescue breath or the simplified version called hands-only CPR. In this detailed guide, we will focus on the hands-only CPR technique based on chest compressions alone, making it easier and accessible to anyone, regardless of prior training or experience, so keep reading to learn more.
What is Hands-Only CPR
The technique known as hands-only CPR involves performing repeated chest compressions on a person who has experienced a sudden cardiac arrest. It is perceived as a simpler CPR method because it eliminates the need for mouth-to-mouth rescue breaths, allowing individuals to focus solely on providing chest compressions.
The compressions help circulate oxygenated blood throughout the body so all the vital organs, including the brain and heart, get sufficient blood supply. The main purpose of hands-only CPR is to “buy time” and keep the person alive until the professional medical team arrives. In that manner, hands-only CPR increases the chances of survival.
Is Hands-Only CPR a Useful Skill?
As up to 70% of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur at home, the importance of knowing hands-only CPR or having a full-on CPR certification can sometimes save the life of a loved one. That is why it is safe to say that learning hands-Only CPR as a life-saving skill offers numerous benefits.
Firstly, individuals are more empowered to take immediate action in emergencies when only chest compressions are involved. Knowing this action can potentially save the life of a family member, a loved one, a colleague, or a stranger is the primary motivator. Secondly, hands-only CPR is easy to learn and remember, increasing the likelihood of its successful implementation in high-stress situations.
That is why it’s important to spread awareness and teach others this technique, as it can lead to a ripple effect of preparedness within the communities. Many believe that getting a CPR certification not only enhances personal knowledge and skills but also contributes to building a safer and more resilient society.
Hands-Only CPR vs. Traditional CPR Technique
The main difference between hands-only CPR and traditional CPR are the rescue breaths. In traditional CPR, rescuers alternate between chest compressions and rescue breaths to deliver oxygen to the victim’s lungs.
However, hands-only CPR skips some CPR steps and excludes the rescue breaths component, simplifying the technique and making it easier for bystanders to initiate emergency response. This modification eliminates potential concerns of disease transmission or hesitations associated with mouth-to-mouth ventilation, making hands-only CPR more accessible and less intimidating for the general public.
When to Use Hands-Only CPR?
Hands-only CPR is recommended to use when a teen or an adult suddenly collapses and is unresponsive, especially if the bystander is not trained in traditional CPR or is uncomfortable performing rescue breaths.
It’s important to note that hands-only CPR has the biggest effect within the first few minutes after the occurrence of a cardiac arrest. The faster the intervention, the higher the likelihood of the victim’s survival. Knowing when to apply Hands-Only CPR steps can help bystander confidence to respond in emergencies and provide life-saving skills to those in need.
CPR Guidelines
When performing hands-only CPR there is a series of CPR steps that need to be implemented in order to aid a person experiencing sudden cardiac arrest. The hands-only CPR steps to effectively administer chest compressions are presented below.
Step-By-Step Hands-Only
1. Check the situation and then the person
Ensuring your personal safety before approaching the victim, and only after checking the person experiencing the emergency and assessing if the situation requires CPR technique. Call for emergency medical assistance. If the person is unresponsive, you likely need to proceed with hands-only CPR. However, you should immediately call for emergency medical assistance or ask someone nearby to do so.
2. Taking the right positioning
Before you start with the chest compressions, position the victim properly by placing them on their back on a firm surface. Make sure that their shoulders are supported, and their chest is exposed.
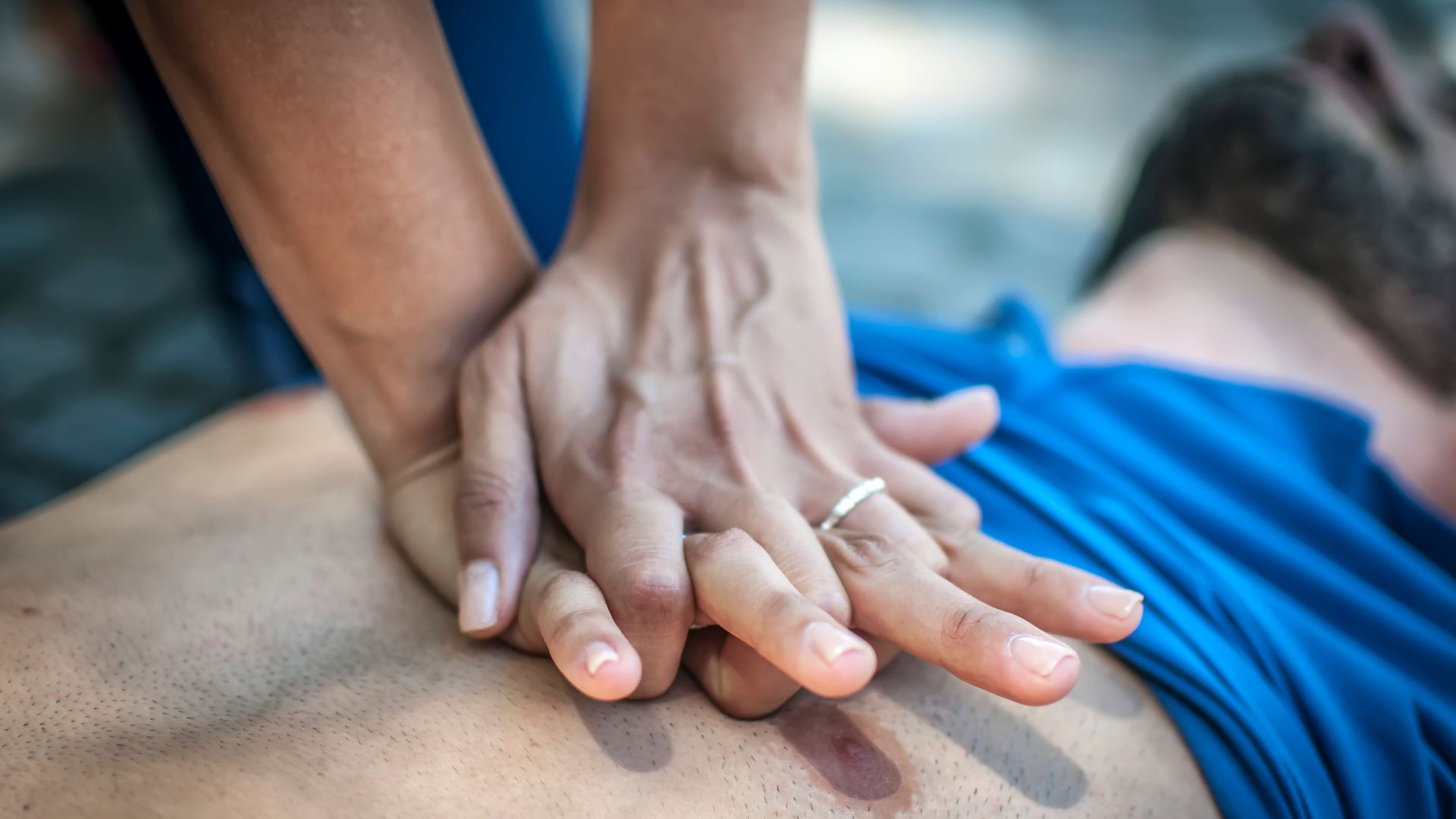
3. Start hands-only CPR technique
Start performing chest compressions by positioning your hand in the center of the victim’s chest, between the nipples. Place your other hand on the top, and interlock your fingers. Lean over the victim and position your shoulders directly above your hands. Begin pressing down firmly and quickly, allowing the chest to recoil between compressions fully.
4. Keep a correct compression rate
Compress the chest at a rate of around 100-120 compressions per minute. Aim for an approximately 2-2.4 inches depth for adults, and give the chest space to rise fully between each compression.
5. Use an AED
Use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if available. You can apply the AED pads to the victim’s chest and follow the device’s instructions for delivering shocks, if necessary.
Tips for Proper Implementation of Hands-Only CPR steps
- Make sure that you are not performing the chest compressions with insufficient depth or rate of compressions.
- You should maintain a steady rhythm and speed while compressing the chest.
- It’s best not to interrupt or pause chest compressions in order to have the biggest probability of successful CPR. The maximum interruption interval should not exceed 10 seconds.
- Make sure that you have placed your hands correctly on the chest of the victim.
- Regularly reassess the victim’s responsiveness and adjust your efforts accordingly.
- Use your body weight to help generate sufficient force during compressions, with a target depth of at least 2 inches, as previously mentioned.
- If you are interested in getting trained you can get CPR certification to increase your confidence in case an emergency response is needed
Additional Considerations for the CPR Technique
There are a couple of things that one needs to consider when analyzing the topic of hands-only CPR guidelines in extensive detail. Here are some considerations about hands-only CPR.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Hands-Only CPR
While hands-only CPR is a valuable and easily accessible life-saving technique, it is essential to be aware of its potential risks and limitations. One significant limitation is that hands-only CPR does not address the need for rescue breaths.
Rescue breaths are crucial for providing oxygen to the victim’s lungs and ensuring optimal oxygenation. Without proper ventilation, the victim’s chances of survival may decrease. Additionally, hands-only CPR may not be suitable for all situations.
For example, if the victim has experienced a drowning incident or a respiratory arrest, the inclusion of rescue breaths becomes vital. In such cases, traditional CPR, which combines chest compressions with rescue breaths, should be initiated promptly.
When to Transition from Hands-Only CPR to Traditional CPR
Recognizing when to transition from hands-only CPR to traditional CPR is crucial for optimizing the chances of survival. Moving to the traditional CPR technique is recommended when advanced medical help is not readily available, or the rescuer is trained and confident in providing rescue breaths.
Also, if the victim is a child or an infant, a full CPR technique is better suited. When the victim is suffering from a respiratory arrest or a drowning incident, traditional CPR with rescue breaths should be preferred.
Importance of CPR Certification
CPR certification and training are essential for anyone who wants to be prepared to respond effectively in emergencies. Hands-only CPR can be easily learned and performed by individuals without formal certification.
However, acquiring CPR certification provides comprehensive training, covering both hands-only CPR and traditional CPR techniques, including rescue breaths. CPR certification courses offer hands-on practice, simulation exercises, and knowledge assessments to ensure participants gain the necessary skills and confidence to respond effectively in cardiac emergencies.
Conclusion
Hands-only CPR is a life-saving skill, and even though the traditional CPR technique is taking the process one step further, still hand-only CPR can double and even triple the survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Of course, CPR certification and training provide a more comprehensive understanding of CPR techniques, including hands-only CPR but also rescue breaths. Whatever CPR level you are more comfortable with, it’s essential for more individuals to possess CPR skills, as hands to the heart can save lives! As more people get familiarized with CPR, the more responsible and safe the societies and cities across the country will be, as the people will always be ready for emergency response.